The Science of Play: How Play-Based Learning Fuels Early Development

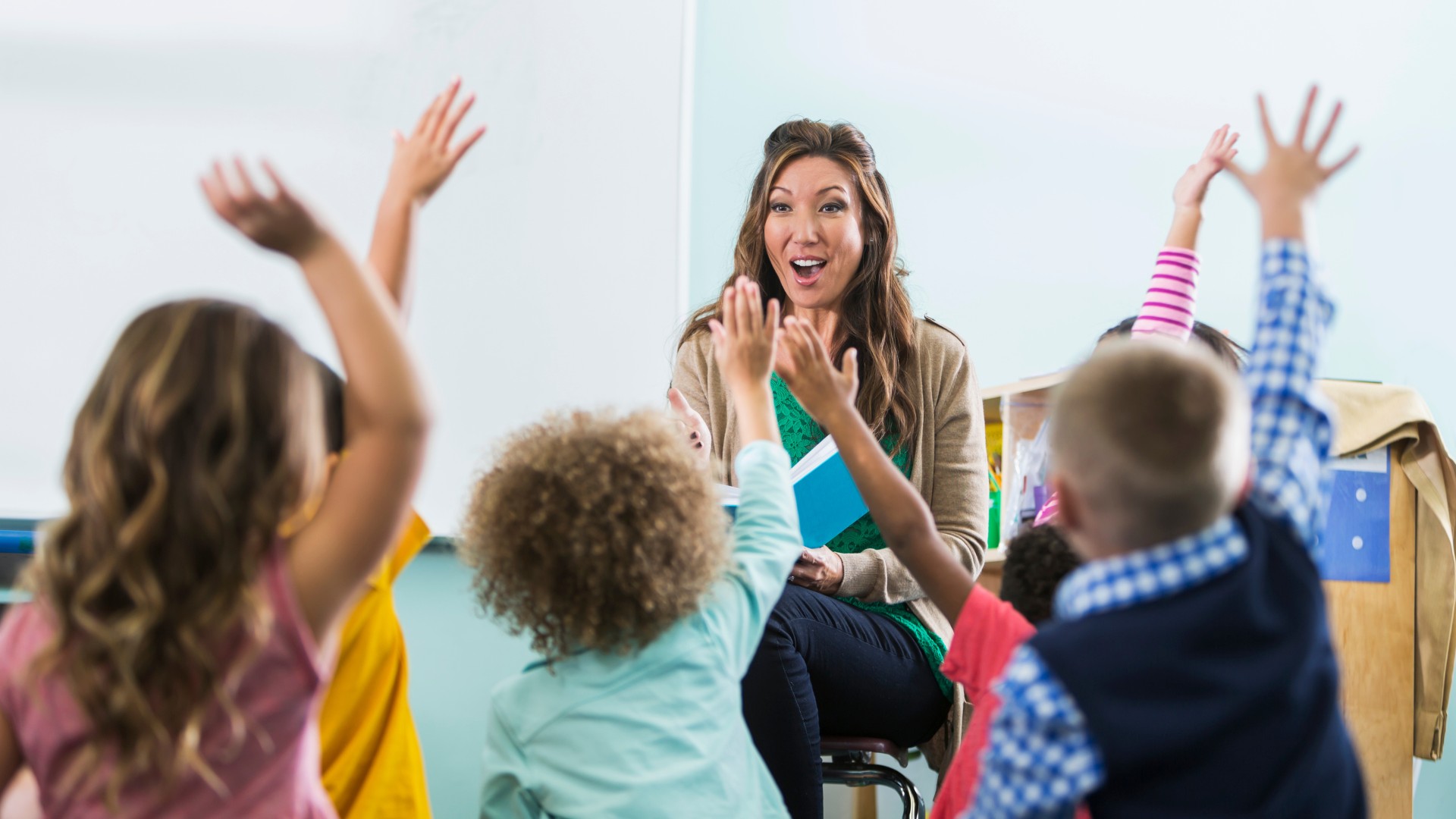
Play is often seen as a simple activity that children engage in for fun, but in the world of early childhood education, it is so much more than that. Play is a powerful tool that drives cognitive, social, emotional, and physical development. At Play Laugh and Grow Academy, we understand that play-based learning is a fundamental approach to helping children develop essential skills that will serve them throughout their lives. In this blog post, we’ll explore the science behind play-based learning and why it is vital for a child’s early development.
The Neuroscience Behind Play-Based Learning
Studies have shown that during early childhood, a child’s brain undergoes significant growth and development. The experiences they have in these early years directly impact how their brain forms connections that shape their ability to learn, process information, and interact with others. When children engage in play, especially play that is interactive and unstructured, they activate multiple areas of their brain. This not only strengthens neural connections but also enhances cognitive functions such as problem-solving, memory, and attention.
For example, when children build with blocks, solve puzzles, or pretend to be characters in a play scenario, they are using their imagination, critical thinking, and spatial reasoning abilities. Play-based activities like these promote the development of executive functions, which include skills such as planning, organizing, and impulse control.
The Role of Play in Emotional and Social Development
While play nurtures cognitive development, it also plays an essential role in emotional and social growth. As children engage in play, they learn how to express their emotions, navigate social interactions, and resolve conflicts. Whether it’s a game of pretend, cooperative play, or a group activity, children learn about empathy, cooperation, and communication. They begin to understand how to share, take turns, and negotiate with their peers.
For instance, when children participate in role-playing activities, they can explore different emotions and practice social scenarios that they may encounter in real life. This kind of play helps children build emotional resilience and become more comfortable expressing themselves in various social settings.
Physical Development Through Play
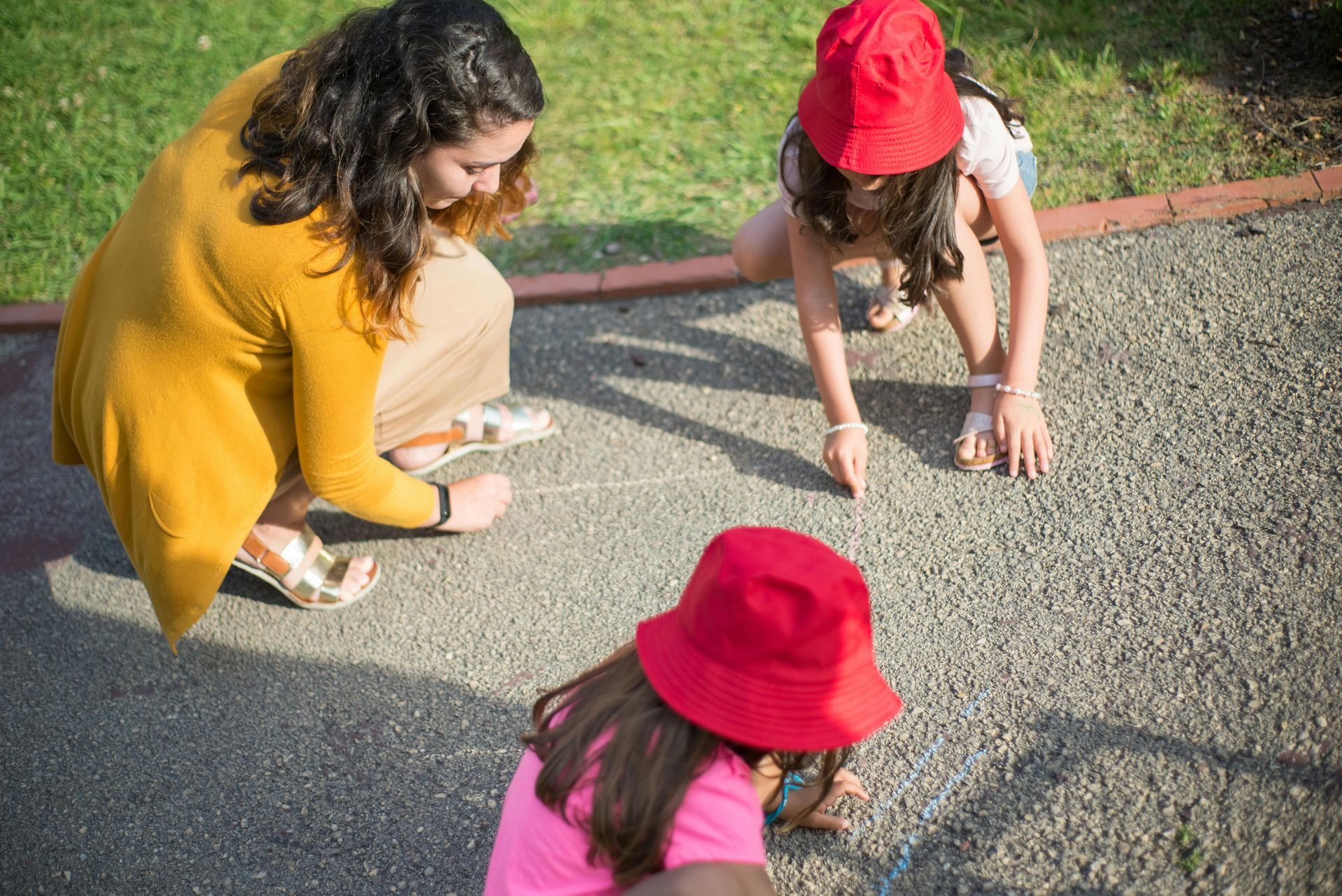
Physical activity is another critical aspect of play-based learning. Gross motor skills, such as running, jumping, and climbing, are developed through active play. These activities help strengthen muscles and coordination while improving balance and overall physical health. Additionally, fine motor skills such as grasping, manipulating small objects, and drawing are cultivated through play-based tasks that require precision and dexterity.
Outdoor play, such as running around in a park or playing ball games, promotes physical health, which is linked to better cognitive function and emotional well-being. Children who engage in physical activity are more likely to have higher levels of concentration and mental clarity, making them better equipped to learn and solve problems.
Encouraging Creativity Through Play
Creativity is another area where play plays a pivotal role. In the early years, children are naturally curious and have vivid imaginations. Play-based learning encourages children to think outside the box and explore their creativity. Whether it’s through arts and crafts, building structures, or storytelling, children are provided with opportunities to experiment, innovate, and express themselves creatively.
At Play Laugh and Grow Academy, we understand that fostering creativity in young children is essential for their long-term success. By encouraging imaginative play, we provide an environment where children can think critically, solve problems, and express their unique ideas.
Why Play-Based Learning Works
The key to the effectiveness of play-based learning lies in its alignment with the way children naturally learn. Children are naturally curious and driven to explore the world around them. When they are allowed to engage in self-directed play, they are actively involved in their learning process. Play provides children with the opportunity to explore concepts, test out new ideas, and learn through trial and error—all of which are essential to cognitive development.
Moreover, play-based learning is flexible and adaptable. It can be tailored to meet the individual needs of each child. Whether it’s providing opportunities for solitary play, cooperative activities, or guided exploration, play-based learning allows children to take ownership of their learning journey.
Conclusion
At Play Laugh and Grow Academy, we recognize the importance of play in early childhood education. Play is not just an activity—it is the foundation for learning. Through play-based activities, children develop the cognitive, social, emotional, and physical skills they need to thrive in life. By creating a play-rich environment, we help children unlock their full potential and build a solid foundation for future success.